2.设 f(x)= dfrac (sqrt {a)-sqrt (a-x)}(x),xlt 0 (agt 0), 当a取何值时,f(x )在 x=0 处连续.-|||-dfrac (cos x)(x+2),xgeqslant 0
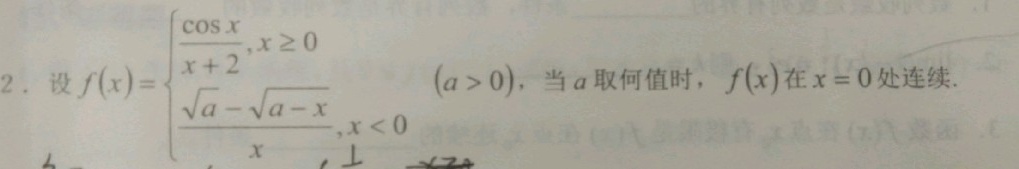
题目解答
答案
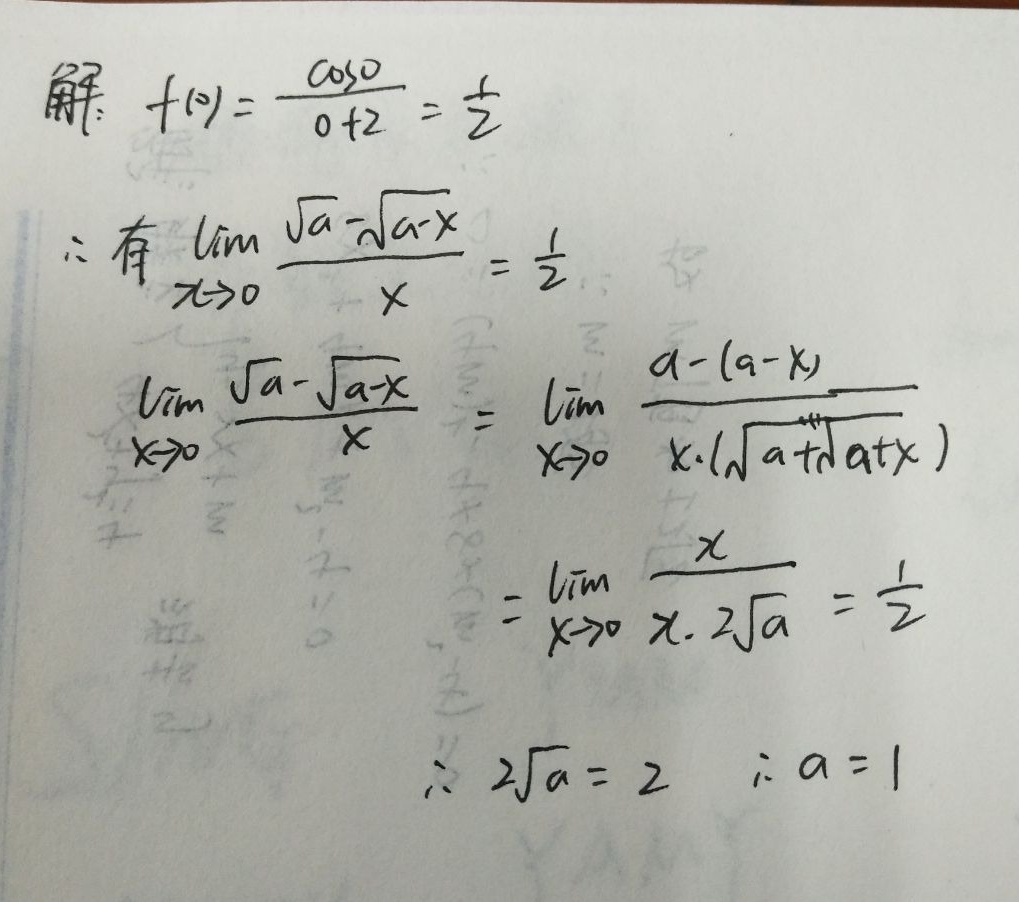
解析
考查要点:本题主要考查函数在分段点处的连续性条件,涉及极限的计算和方程求解。
解题核心思路:
- 连续性条件:函数在$x=0$处连续需满足左极限、右极限均存在且等于$f(0)$。
- 右极限直接计算:当$x \geq 0$时,$f(x) = \frac{\cos x}{x+2}$,代入$x=0$即可得右极限。
- 左极限化简:当$x < 0$时,分子为$\sqrt{a} - \sqrt{a - x}$,通过有理化或洛必达法则化简后求极限。
- 方程求解:令左极限等于$f(0)$,解关于$a$的方程。
破题关键:
- 有理化处理分子,将分式化简为可直接求极限的形式。
- 正确处理极限表达式,注意$x \to 0$时$\sqrt{a - x} \to \sqrt{a}$。
步骤1:计算$f(0)$
当$x \geq 0$时,$f(x) = \frac{\cos x}{x+2}$,代入$x=0$得:
$f(0) = \frac{\cos 0}{0 + 2} = \frac{1}{2}.$
步骤2:计算右极限$\lim_{x \to 0^+} f(x)$
当$x \to 0^+$时,$f(x) = \frac{\cos x}{x+2}$,直接代入$x=0$得:
$\lim_{x \to 0^+} f(x) = \frac{\cos 0}{0 + 2} = \frac{1}{2}.$
步骤3:计算左极限$\lim_{x \to 0^-} f(x)$
当$x \to 0^-$时,$f(x) = \frac{\sqrt{a} - \sqrt{a - x}}{x}$。通过有理化分子:
$\begin{aligned}\lim_{x \to 0^-} f(x) &= \lim_{x \to 0^-} \frac{\sqrt{a} - \sqrt{a - x}}{x} \\&= \lim_{x \to 0^-} \frac{(\sqrt{a} - \sqrt{a - x})(\sqrt{a} + \sqrt{a - x})}{x (\sqrt{a} + \sqrt{a - x})} \\&= \lim_{x \to 0^-} \frac{a - (a - x)}{x (\sqrt{a} + \sqrt{a - x})} \\&= \lim_{x \to 0^-} \frac{x}{x (\sqrt{a} + \sqrt{a - x})} \\&= \lim_{x \to 0^-} \frac{1}{\sqrt{a} + \sqrt{a - x}} \\&= \frac{1}{\sqrt{a} + \sqrt{a}} = \frac{1}{2\sqrt{a}}.\end{aligned}$
步骤4:令左极限等于$f(0)$
根据连续性条件,左极限需等于$f(0) = \frac{1}{2}$,即:
$\frac{1}{2\sqrt{a}} = \frac{1}{2} \implies \sqrt{a} = 1 \implies a = 1.$