题目
3、已知 lim _(xarrow 0)((1-dfrac {x)(2))}^dfrac (a{x)}=(e)^2, 则常数 a= __

题目解答
答案
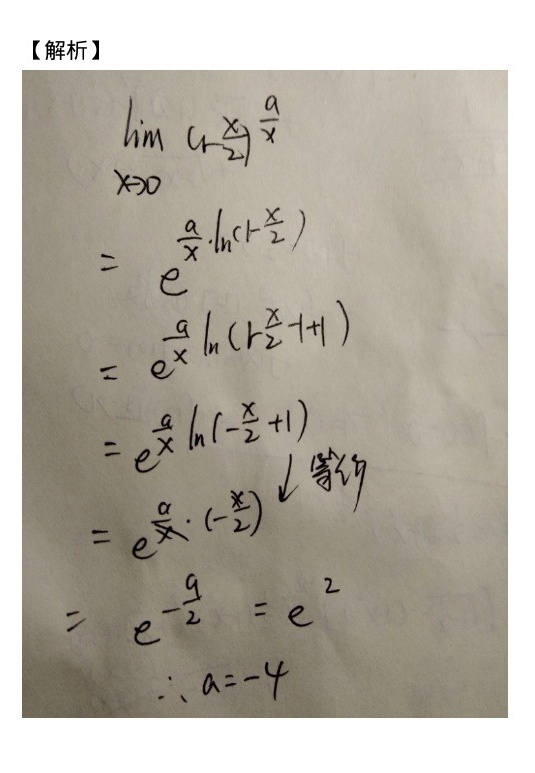
解析
步骤 1:利用极限的性质
根据极限的性质,当 $x$ 趋近于 $0$ 时,$(1-\dfrac{x}{2})^{\dfrac{a}{x}}$ 的极限可以表示为 $e$ 的幂次形式。即,$\lim_{x\rightarrow 0}{(1-\dfrac{x}{2})}^{\dfrac{a}{x}} = e^{\lim_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{a}{x}\ln(1-\dfrac{x}{2})}$。
步骤 2:计算极限
计算 $\lim_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{a}{x}\ln(1-\dfrac{x}{2})$。由于 $\ln(1-\dfrac{x}{2})$ 在 $x$ 趋近于 $0$ 时可以近似为 $-\dfrac{x}{2}$,因此 $\lim_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{a}{x}\ln(1-\dfrac{x}{2}) = \lim_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{a}{x}(-\dfrac{x}{2}) = -\dfrac{a}{2}$。
步骤 3:确定常数 $a$
根据题目条件,$\lim_{x\rightarrow 0}{(1-\dfrac{x}{2})}^{\dfrac{a}{x}} = e^2$,因此 $e^{-\dfrac{a}{2}} = e^2$。由此可得 $-\dfrac{a}{2} = 2$,从而解得 $a = -4$。
根据极限的性质,当 $x$ 趋近于 $0$ 时,$(1-\dfrac{x}{2})^{\dfrac{a}{x}}$ 的极限可以表示为 $e$ 的幂次形式。即,$\lim_{x\rightarrow 0}{(1-\dfrac{x}{2})}^{\dfrac{a}{x}} = e^{\lim_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{a}{x}\ln(1-\dfrac{x}{2})}$。
步骤 2:计算极限
计算 $\lim_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{a}{x}\ln(1-\dfrac{x}{2})$。由于 $\ln(1-\dfrac{x}{2})$ 在 $x$ 趋近于 $0$ 时可以近似为 $-\dfrac{x}{2}$,因此 $\lim_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{a}{x}\ln(1-\dfrac{x}{2}) = \lim_{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac{a}{x}(-\dfrac{x}{2}) = -\dfrac{a}{2}$。
步骤 3:确定常数 $a$
根据题目条件,$\lim_{x\rightarrow 0}{(1-\dfrac{x}{2})}^{\dfrac{a}{x}} = e^2$,因此 $e^{-\dfrac{a}{2}} = e^2$。由此可得 $-\dfrac{a}{2} = 2$,从而解得 $a = -4$。