题目
设 f(x)= { x,xlt 1 . 若 f(x)在 x=1 处可导,则 a= __ ,=-|||-__
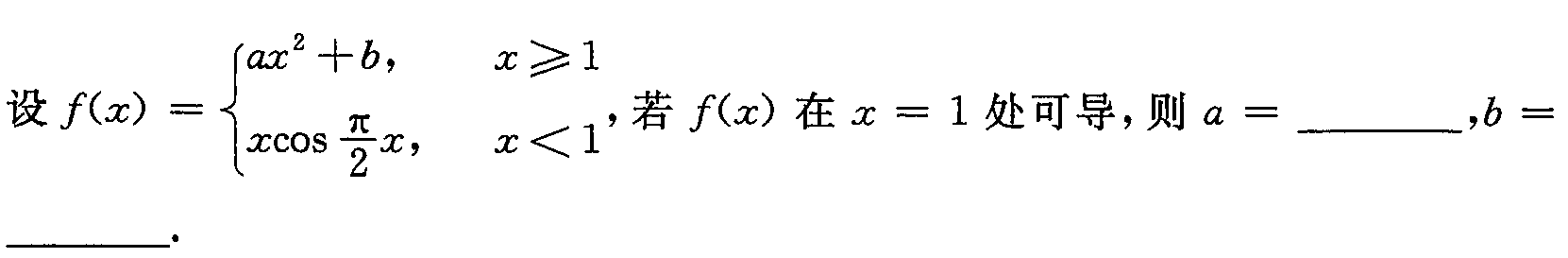
题目解答
答案

解析
步骤 1:确定函数在 x=1 处连续
要使函数 f(x) 在 x=1 处可导,首先需要保证函数在该点连续。这意味着函数在 x=1 处的左极限和右极限必须相等,且等于函数在该点的值。即:
$$\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}f(x)=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}f(x)=f(1)$$
步骤 2:计算函数在 x=1 处的左极限和右极限
根据函数定义,当 x<1 时,f(x) = xcos(π/2)x,当 x≥1 时,f(x) = ax^2 + b。因此,我们有:
$$\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}f(x)=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}(ax^2+b)=a+b$$
$$\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}f(x)=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}(x\cos \dfrac {\pi }{2}x)=1\cos \dfrac {\pi }{2}=0$$
步骤 3:确定 a 和 b 的关系
由于函数在 x=1 处连续,我们有:
$$a+b=0$$
步骤 4:确定函数在 x=1 处的导数
要使函数在 x=1 处可导,函数在该点的左导数和右导数必须相等。即:
$$f'(1)=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}\dfrac {f(x)-f(1)}{x-1}=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}\dfrac {f(x)-f(1)}{x-1}$$
步骤 5:计算函数在 x=1 处的左导数和右导数
根据函数定义,我们有:
$$f'(1)=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}\dfrac {f(x)-f(1)}{x-1}=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}\dfrac {a{x}^{2}+b-(a+b)}{x-1}=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}\dfrac {a{x}^{2}-a}{x-1}=2a$$
$$f'(1)=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}\dfrac {f(x)-f(1)}{x-1}=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}\dfrac {x\cos \dfrac {\pi }{2}x}{x-1}=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}\dfrac {-(x-1)\sin \dfrac {\pi }{2}(x-1)}{x-1}=-\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}\sin \dfrac {\pi }{2}(x-1)=-\dfrac {\pi }{2}$$
步骤 6:确定 a 的值
由于函数在 x=1 处可导,我们有:
$$2a=-\dfrac {\pi }{2}$$
解得:
$$a=-\dfrac {\pi }{4}$$
步骤 7:确定 b 的值
根据步骤 3 中的 a+b=0,我们有:
$$b=-a=\dfrac {\pi }{4}$$
要使函数 f(x) 在 x=1 处可导,首先需要保证函数在该点连续。这意味着函数在 x=1 处的左极限和右极限必须相等,且等于函数在该点的值。即:
$$\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}f(x)=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}f(x)=f(1)$$
步骤 2:计算函数在 x=1 处的左极限和右极限
根据函数定义,当 x<1 时,f(x) = xcos(π/2)x,当 x≥1 时,f(x) = ax^2 + b。因此,我们有:
$$\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}f(x)=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}(ax^2+b)=a+b$$
$$\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}f(x)=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}(x\cos \dfrac {\pi }{2}x)=1\cos \dfrac {\pi }{2}=0$$
步骤 3:确定 a 和 b 的关系
由于函数在 x=1 处连续,我们有:
$$a+b=0$$
步骤 4:确定函数在 x=1 处的导数
要使函数在 x=1 处可导,函数在该点的左导数和右导数必须相等。即:
$$f'(1)=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}\dfrac {f(x)-f(1)}{x-1}=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}\dfrac {f(x)-f(1)}{x-1}$$
步骤 5:计算函数在 x=1 处的左导数和右导数
根据函数定义,我们有:
$$f'(1)=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}\dfrac {f(x)-f(1)}{x-1}=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}\dfrac {a{x}^{2}+b-(a+b)}{x-1}=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{+}}\dfrac {a{x}^{2}-a}{x-1}=2a$$
$$f'(1)=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}\dfrac {f(x)-f(1)}{x-1}=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}\dfrac {x\cos \dfrac {\pi }{2}x}{x-1}=\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}\dfrac {-(x-1)\sin \dfrac {\pi }{2}(x-1)}{x-1}=-\lim _{x\rightarrow {1}^{-}}\sin \dfrac {\pi }{2}(x-1)=-\dfrac {\pi }{2}$$
步骤 6:确定 a 的值
由于函数在 x=1 处可导,我们有:
$$2a=-\dfrac {\pi }{2}$$
解得:
$$a=-\dfrac {\pi }{4}$$
步骤 7:确定 b 的值
根据步骤 3 中的 a+b=0,我们有:
$$b=-a=\dfrac {\pi }{4}$$