题目
设f(x)= ^2),xneq 0 0,x=0 . 求f`(x),并讨论f`(x)在 x=0 处的连续性.
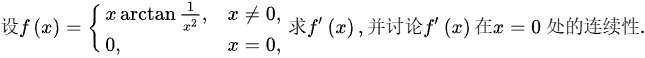
题目解答
答案


解析
步骤 1:求导数 $f'(x)$ 对于 $x\neq 0$
对于 $x\neq 0$, 函数由下式给出: $f(x)=x\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}}$ 我们使用乘积法则来找到导数: $f'(x)=\dfrac {d}{dx}(x\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}})=\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}}+x$ $\dfrac {d}{dx}(\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}})$ 为了找到 $\dfrac {d}{dx}(\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}})$ ,我们使用链式法则: $\dfrac {d}{dx}(\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}})=\dfrac {1}{1+{(\dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}})}^{2}}\cdot \dfrac {d}{dx}(\dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}})=\dfrac {1}{1+\dfrac {1}{{x}^{4}}}\cdot (-\dfrac {2}{{x}^{3}})$ 因此, $f'(x)=\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}}-\dfrac {2{x}^{2}}{{x}^{4}+1}$
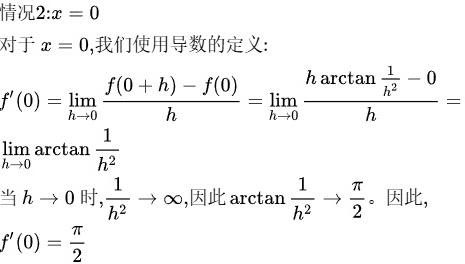
步骤 2:求导数 $f'(x)$ 对于 $x=0$
对于 $x=0$ 我们使用导数的定义: $f'(0)=\lim _{h\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {f(0+h)-f(0)}{h}=\lim _{h\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {h\tan \dfrac {1}{{k}^{2}}-0}{h}=$ $\lim _{h\rightarrow 0}\arctan \dfrac {1}{{h}^{2}}$ 当h→0时, $\dfrac {1}{{h}^{2}}\rightarrow \infty $ ,因此 $\arctan \dfrac {1}{{h}^{2}}\rightarrow \dfrac {\pi }{2}$ 。因此, $f'(0)=\dfrac {\pi }{2}$
步骤 3:讨论 $f'(x)$ 在 $x=0$ 处的连续性
要检查 $f'(x)$ 在 $x=0$ 处的连续性,我们需要看 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}f'(x)=f'(0)$ = 我们已经得到: $f'(x)=\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}}-\dfrac {2{x}^{2}}{{x}^{4}+1}$ 对于 $x\neq 0$ 当x→0时, $\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}}\rightarrow \dfrac {\pi }{2}$ $\dfrac {2{x}^{2}}{{x}^{4}+1}\rightarrow 0$ 因此, $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}f'(x)=\dfrac {\pi }{2}-0=\dfrac {\pi }{2}$ 所以 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}f'(x)=f'(0)=\dfrac {\pi }{2}$ , $f'(x)$ 在 $x=0$ 处连续
对于 $x\neq 0$, 函数由下式给出: $f(x)=x\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}}$ 我们使用乘积法则来找到导数: $f'(x)=\dfrac {d}{dx}(x\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}})=\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}}+x$ $\dfrac {d}{dx}(\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}})$ 为了找到 $\dfrac {d}{dx}(\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}})$ ,我们使用链式法则: $\dfrac {d}{dx}(\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}})=\dfrac {1}{1+{(\dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}})}^{2}}\cdot \dfrac {d}{dx}(\dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}})=\dfrac {1}{1+\dfrac {1}{{x}^{4}}}\cdot (-\dfrac {2}{{x}^{3}})$ 因此, $f'(x)=\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}}-\dfrac {2{x}^{2}}{{x}^{4}+1}$
步骤 2:求导数 $f'(x)$ 对于 $x=0$
对于 $x=0$ 我们使用导数的定义: $f'(0)=\lim _{h\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {f(0+h)-f(0)}{h}=\lim _{h\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {h\tan \dfrac {1}{{k}^{2}}-0}{h}=$ $\lim _{h\rightarrow 0}\arctan \dfrac {1}{{h}^{2}}$ 当h→0时, $\dfrac {1}{{h}^{2}}\rightarrow \infty $ ,因此 $\arctan \dfrac {1}{{h}^{2}}\rightarrow \dfrac {\pi }{2}$ 。因此, $f'(0)=\dfrac {\pi }{2}$
步骤 3:讨论 $f'(x)$ 在 $x=0$ 处的连续性
要检查 $f'(x)$ 在 $x=0$ 处的连续性,我们需要看 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}f'(x)=f'(0)$ = 我们已经得到: $f'(x)=\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}}-\dfrac {2{x}^{2}}{{x}^{4}+1}$ 对于 $x\neq 0$ 当x→0时, $\arctan \dfrac {1}{{x}^{2}}\rightarrow \dfrac {\pi }{2}$ $\dfrac {2{x}^{2}}{{x}^{4}+1}\rightarrow 0$ 因此, $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}f'(x)=\dfrac {\pi }{2}-0=\dfrac {\pi }{2}$ 所以 $\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}f'(x)=f'(0)=\dfrac {\pi }{2}$ , $f'(x)$ 在 $x=0$ 处连续