题目
确定下列函数的单调区间: =ln (x+sqrt (1+{x)^2})
确定下列函数的单调区间:
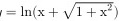
题目解答
答案
因为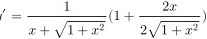
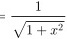
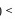 , 所以函数在
, 所以函数在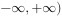 内单调增加,无单调减区间。
内单调增加,无单调减区间。
解析
步骤 1:求导
首先,我们需要求出函数$f(x) = \ln (x+\sqrt {1+x^{2}})$的导数。根据链式法则,我们有:
$$f'(x) = \frac{1}{x+\sqrt{1+x^{2}}} \cdot \left(1 + \frac{2x}{2\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}\right)$$
步骤 2:化简导数
化简导数表达式,得到:
$$f'(x) = \frac{1}{x+\sqrt{1+x^{2}}} \cdot \left(1 + \frac{x}{\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}\right)$$
$$f'(x) = \frac{1}{x+\sqrt{1+x^{2}}} \cdot \frac{x+\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}{\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}$$
$$f'(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}$$
步骤 3:分析导数符号
由于$\sqrt{1+x^{2}}$总是正的,因此$f'(x)$总是正的。这意味着函数$f(x)$在其定义域内是单调增加的。
首先,我们需要求出函数$f(x) = \ln (x+\sqrt {1+x^{2}})$的导数。根据链式法则,我们有:
$$f'(x) = \frac{1}{x+\sqrt{1+x^{2}}} \cdot \left(1 + \frac{2x}{2\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}\right)$$
步骤 2:化简导数
化简导数表达式,得到:
$$f'(x) = \frac{1}{x+\sqrt{1+x^{2}}} \cdot \left(1 + \frac{x}{\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}\right)$$
$$f'(x) = \frac{1}{x+\sqrt{1+x^{2}}} \cdot \frac{x+\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}{\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}$$
$$f'(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}$$
步骤 3:分析导数符号
由于$\sqrt{1+x^{2}}$总是正的,因此$f'(x)$总是正的。这意味着函数$f(x)$在其定义域内是单调增加的。