题目
设 函数 f ( x ) 在 x = 0 处可导,且lim _(xarrow 0)dfrac (f(2x)-f(0))(ln (1+3x))=1,则f'(0)=( )lim _(xarrow 0)dfrac (f(2x)-f(0))(ln (1+3x))=1
设 函数 f ( x ) 在 x = 0 处可导,且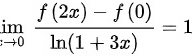 ,则f'(0)=( )
,则f'(0)=( )
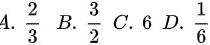
题目解答
答案
解:
∵x→0
∴由等价无穷小替换得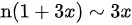
∴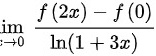
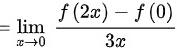
∵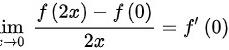
∴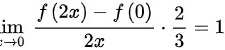
即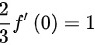
∴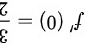
故选B
解析
步骤 1:等价无穷小替换
由于当$x\rightarrow 0$时,$\ln(1+3x)$与$3x$是等价无穷小,因此可以将$\ln(1+3x)$替换为$3x$。
步骤 2:代入等价无穷小
将$\ln(1+3x)$替换为$3x$,得到$\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {f(2x)-f(0)}{3x}$。
步骤 3:利用导数定义
根据导数的定义,$\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {f(2x)-f(0)}{2x}=f'(0)$,因此$\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {f(2x)-f(0)}{3x}=\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {f(2x)-f(0)}{2x}\cdot \dfrac {2}{3}=f'(0)\cdot \dfrac {2}{3}$。
步骤 4:求解f'(0)
根据题目条件,$\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {f(2x)-f(0)}{\ln (1+3x)}=1$,因此$f'(0)\cdot \dfrac {2}{3}=1$,解得$f'(0)=\dfrac {3}{2}$。
由于当$x\rightarrow 0$时,$\ln(1+3x)$与$3x$是等价无穷小,因此可以将$\ln(1+3x)$替换为$3x$。
步骤 2:代入等价无穷小
将$\ln(1+3x)$替换为$3x$,得到$\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {f(2x)-f(0)}{3x}$。
步骤 3:利用导数定义
根据导数的定义,$\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {f(2x)-f(0)}{2x}=f'(0)$,因此$\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {f(2x)-f(0)}{3x}=\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {f(2x)-f(0)}{2x}\cdot \dfrac {2}{3}=f'(0)\cdot \dfrac {2}{3}$。
步骤 4:求解f'(0)
根据题目条件,$\lim _{x\rightarrow 0}\dfrac {f(2x)-f(0)}{\ln (1+3x)}=1$,因此$f'(0)\cdot \dfrac {2}{3}=1$,解得$f'(0)=\dfrac {3}{2}$。