(4) lim _(xarrow 1)dfrac ({x)^2-sqrt (x)}(sqrt {x)-1};
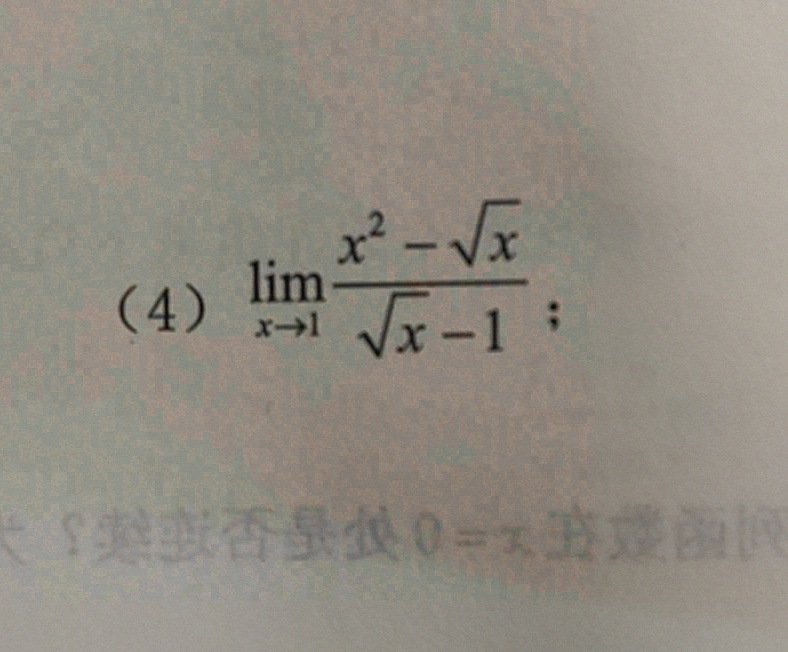
题目解答
答案

解析
考查要点:本题主要考查极限的计算方法,特别是处理$\frac{0}{0}$型不定式的能力。需要掌握分母有理化或洛必达法则的应用。
解题核心思路:
当直接代入$x=1$导致分母为0时,需通过变形消除不定式。
- 分母有理化:通过乘以共轭根式$\sqrt{x}+1$,将分母转化为$x-1$,再分解分子中的因式$(x-1)$。
- 洛必达法则:若分子分母同时趋近于0,可对分子分母分别求导后重新求极限。
破题关键点:
- 识别$\frac{0}{0}$型不定式,选择合适方法。
- 分子展开后,正确分解因式$(x-1)$以约分。
- 洛必达法则应用时,正确计算导数并化简。
法1:分母有理化
-
有理化分母:
分子分母同乘$\sqrt{x}+1$,得:
$\lim _{x\rightarrow 1}\dfrac {({x}^{2}-\sqrt {x})(\sqrt {x}+1)}{(\sqrt {x}-1)(\sqrt {x}+1)} = \lim _{x\rightarrow 1}\dfrac {({x}^{2}-\sqrt {x})(\sqrt {x}+1)}{x-1}$ -
展开分子:
分子展开为:
${x}^{2}\sqrt{x} + {x}^{2} - \sqrt{x} \cdot \sqrt{x} - \sqrt{x} = x^{5/2} + x^2 - x - \sqrt{x}$ -
分解因式:
将分子拆分为两部分:
$\sqrt{x}(x^2 - 1) + x(x - 1)$
其中$x^2 - 1 = (x-1)(x+1)$,因此:
$\sqrt{x}(x-1)(x+1) + x(x-1)$ -
约分并求极限:
分母为$x-1$,约分后得:
$\lim _{x\rightarrow 1} \left[ \sqrt{x}(x+1) + x \right] = \sqrt{1}(1+1) + 1 = 3$
法2:洛必达法则
-
验证条件:
当$x \to 1$时,分子$x^2 - \sqrt{x} \to 0$,分母$\sqrt{x} - 1 \to 0$,满足$\frac{0}{0}$型。 -
求导分子分母:
- 分子导数:$\dfrac{d}{dx}(x^2 - \sqrt{x}) = 2x - \dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}$
- 分母导数:$\dfrac{d}{dx}(\sqrt{x} - 1) = \dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}$
-
应用洛必达法则:
$\lim _{x\rightarrow 1} \dfrac{2x - \dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}}{\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}} = \lim _{x\rightarrow 1} \left(4x\sqrt{x} - 1\right) = 4 \cdot 1 \cdot 1 - 1 = 3$