题目
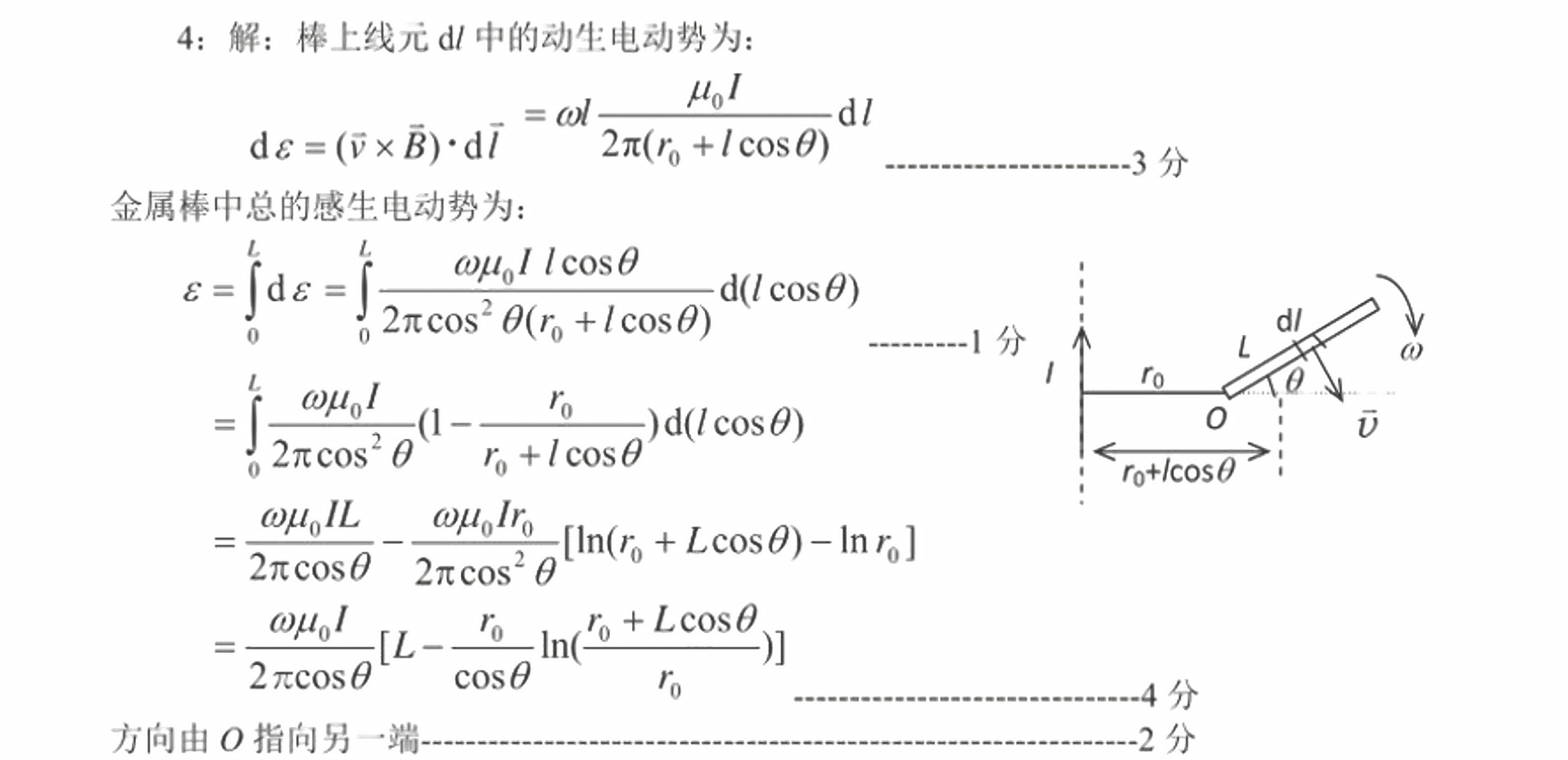
4:一无限长竖直导线上通有稳定电流I,电流方向向上。导线旁有一与导线共面、长-|||-度为L的金属棒,绕其一端O在该平面内顺时针匀速转动,如图所示。转动角速度为w,O-|||-点到导线的垂直距离为 _(0)((r)_(0)gt L) 。试求金属棒转到与水平面成θ角时,棒内感应电动势的大-|||-小和方向。-|||-I , θ w-|||-L-|||-0-|||-kro-|||-2327图

题目解答
答案
解析
步骤 1:确定动生电动势的表达式
金属棒在磁场中运动时,棒上的每个微小线元 $dl$ 会产生动生电动势 $d\epsilon$。根据法拉第电磁感应定律,动生电动势可以表示为:
$$
d\epsilon = (\overline{v} \times \overline{B}) \cdot d\overline{l}
$$
其中,$\overline{v}$ 是线元的速度,$\overline{B}$ 是线元所在位置的磁场强度,$d\overline{l}$ 是线元的长度向量。由于金属棒绕O点转动,线元的速度 $\overline{v} = \omega l \cos \theta \hat{k}$,其中 $\omega$ 是角速度,$l$ 是线元到O点的距离,$\theta$ 是金属棒与水平面的夹角,$\hat{k}$ 是垂直于导线和金属棒平面的单位向量。磁场强度 $\overline{B} = \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi (r_0 + l \cos \theta)} \hat{k}$,其中 $\mu_0$ 是真空磁导率,$I$ 是导线中的电流,$r_0$ 是O点到导线的垂直距离。因此,动生电动势可以表示为:
$$
d\epsilon = \omega \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi (r_0 + l \cos \theta)} dl
$$
步骤 2:计算总的感应电动势
总的感应电动势 $\epsilon$ 是所有线元动生电动势的积分,即:
$$
\epsilon = \int_0^L d\epsilon = \int_0^L \omega \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi (r_0 + l \cos \theta)} dl
$$
为了计算这个积分,我们先将积分变量从 $l$ 转换为 $x = r_0 + l \cos \theta$,则 $dl = \frac{dx}{\cos \theta}$。因此,积分变为:
$$
\epsilon = \int_{r_0}^{r_0 + L \cos \theta} \omega \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi x} \frac{dx}{\cos \theta} = \frac{\omega \mu_0 I}{2\pi \cos \theta} \int_{r_0}^{r_0 + L \cos \theta} \frac{dx}{x}
$$
这个积分是一个对数积分,结果为:
$$
\epsilon = \frac{\omega \mu_0 I}{2\pi \cos \theta} \left[ \ln x \right]_{r_0}^{r_0 + L \cos \theta} = \frac{\omega \mu_0 I}{2\pi \cos \theta} \left[ \ln (r_0 + L \cos \theta) - \ln r_0 \right]
$$
简化后得到:
$$
\epsilon = \frac{\omega \mu_0 I}{2\pi \cos \theta} \ln \left( \frac{r_0 + L \cos \theta}{r_0} \right)
$$
步骤 3:确定感应电动势的方向
根据右手定则,感应电动势的方向由O指向金属棒的另一端。
金属棒在磁场中运动时,棒上的每个微小线元 $dl$ 会产生动生电动势 $d\epsilon$。根据法拉第电磁感应定律,动生电动势可以表示为:
$$
d\epsilon = (\overline{v} \times \overline{B}) \cdot d\overline{l}
$$
其中,$\overline{v}$ 是线元的速度,$\overline{B}$ 是线元所在位置的磁场强度,$d\overline{l}$ 是线元的长度向量。由于金属棒绕O点转动,线元的速度 $\overline{v} = \omega l \cos \theta \hat{k}$,其中 $\omega$ 是角速度,$l$ 是线元到O点的距离,$\theta$ 是金属棒与水平面的夹角,$\hat{k}$ 是垂直于导线和金属棒平面的单位向量。磁场强度 $\overline{B} = \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi (r_0 + l \cos \theta)} \hat{k}$,其中 $\mu_0$ 是真空磁导率,$I$ 是导线中的电流,$r_0$ 是O点到导线的垂直距离。因此,动生电动势可以表示为:
$$
d\epsilon = \omega \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi (r_0 + l \cos \theta)} dl
$$
步骤 2:计算总的感应电动势
总的感应电动势 $\epsilon$ 是所有线元动生电动势的积分,即:
$$
\epsilon = \int_0^L d\epsilon = \int_0^L \omega \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi (r_0 + l \cos \theta)} dl
$$
为了计算这个积分,我们先将积分变量从 $l$ 转换为 $x = r_0 + l \cos \theta$,则 $dl = \frac{dx}{\cos \theta}$。因此,积分变为:
$$
\epsilon = \int_{r_0}^{r_0 + L \cos \theta} \omega \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi x} \frac{dx}{\cos \theta} = \frac{\omega \mu_0 I}{2\pi \cos \theta} \int_{r_0}^{r_0 + L \cos \theta} \frac{dx}{x}
$$
这个积分是一个对数积分,结果为:
$$
\epsilon = \frac{\omega \mu_0 I}{2\pi \cos \theta} \left[ \ln x \right]_{r_0}^{r_0 + L \cos \theta} = \frac{\omega \mu_0 I}{2\pi \cos \theta} \left[ \ln (r_0 + L \cos \theta) - \ln r_0 \right]
$$
简化后得到:
$$
\epsilon = \frac{\omega \mu_0 I}{2\pi \cos \theta} \ln \left( \frac{r_0 + L \cos \theta}{r_0} \right)
$$
步骤 3:确定感应电动势的方向
根据右手定则,感应电动势的方向由O指向金属棒的另一端。