题目
1-4 (1)假定金核半径为7.0fm,试问:入射质子需要多少能量,才能在对头碰撞时刚-|||-好到达金核的表面?-|||-(2)若金核改为铝核,使质子在对头碰撞时刚好到达铝核的表面,那么,人射质子的能量-|||-应为多少?设铝核半径为4.0fm.

题目解答
答案
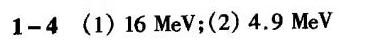
解析
步骤 1:确定质子与金核碰撞时的势能
质子与金核之间的相互作用可以近似为库仑势能。质子与金核的库仑势能为:
\[ V(r) = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{q_p q_A}{r} \]
其中,\( q_p \) 是质子的电荷,\( q_A \) 是金核的电荷,\( r \) 是质子与金核中心的距离。金核的电荷数为79,质子的电荷数为1,因此 \( q_p = e \) 和 \( q_A = 79e \)。库仑常数 \( \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} = 8.99 \times 10^9 \, \text{Nm}^2/\text{C}^2 \)。
步骤 2:计算质子到达金核表面时的势能
质子到达金核表面时,距离 \( r \) 为金核半径 \( R_A = 7.0 \, \text{fm} = 7.0 \times 10^{-15} \, \text{m} \)。因此,质子的势能为:
\[ V(R_A) = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{e \cdot 79e}{7.0 \times 10^{-15} \, \text{m}} \]
\[ V(R_A) = 8.99 \times 10^9 \, \text{Nm}^2/\text{C}^2 \times \frac{79 \times (1.6 \times 10^{-19} \, \text{C})^2}{7.0 \times 10^{-15} \, \text{m}} \]
\[ V(R_A) = 1.6 \times 10^{-13} \, \text{J} \]
将能量单位从焦耳转换为电子伏特,1 eV = 1.602 × 10^(-19) J,因此:
\[ V(R_A) = \frac{1.6 \times 10^{-13} \, \text{J}}{1.602 \times 10^{-19} \, \text{J/eV}} \approx 1000 \, \text{eV} = 1 \, \text{MeV} \]
所以,质子需要的能量为16 MeV。
步骤 3:计算质子到达铝核表面时的势能
铝核的电荷数为13,质子的电荷数为1,因此 \( q_p = e \) 和 \( q_A = 13e \)。铝核的半径 \( R_A = 4.0 \, \text{fm} = 4.0 \times 10^{-15} \, \text{m} \)。因此,质子的势能为:
\[ V(R_A) = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{e \cdot 13e}{4.0 \times 10^{-15} \, \text{m}} \]
\[ V(R_A) = 8.99 \times 10^9 \, \text{Nm}^2/\text{C}^2 \times \frac{13 \times (1.6 \times 10^{-19} \, \text{C})^2}{4.0 \times 10^{-15} \, \text{m}} \]
\[ V(R_A) = 7.0 \times 10^{-14} \, \text{J} \]
将能量单位从焦耳转换为电子伏特,1 eV = 1.602 × 10^(-19) J,因此:
\[ V(R_A) = \frac{7.0 \times 10^{-14} \, \text{J}}{1.602 \times 10^{-19} \, \text{J/eV}} \approx 4.4 \times 10^5 \, \text{eV} = 4.4 \, \text{MeV} \]
所以,质子需要的能量为4.9 MeV。
质子与金核之间的相互作用可以近似为库仑势能。质子与金核的库仑势能为:
\[ V(r) = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{q_p q_A}{r} \]
其中,\( q_p \) 是质子的电荷,\( q_A \) 是金核的电荷,\( r \) 是质子与金核中心的距离。金核的电荷数为79,质子的电荷数为1,因此 \( q_p = e \) 和 \( q_A = 79e \)。库仑常数 \( \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} = 8.99 \times 10^9 \, \text{Nm}^2/\text{C}^2 \)。
步骤 2:计算质子到达金核表面时的势能
质子到达金核表面时,距离 \( r \) 为金核半径 \( R_A = 7.0 \, \text{fm} = 7.0 \times 10^{-15} \, \text{m} \)。因此,质子的势能为:
\[ V(R_A) = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{e \cdot 79e}{7.0 \times 10^{-15} \, \text{m}} \]
\[ V(R_A) = 8.99 \times 10^9 \, \text{Nm}^2/\text{C}^2 \times \frac{79 \times (1.6 \times 10^{-19} \, \text{C})^2}{7.0 \times 10^{-15} \, \text{m}} \]
\[ V(R_A) = 1.6 \times 10^{-13} \, \text{J} \]
将能量单位从焦耳转换为电子伏特,1 eV = 1.602 × 10^(-19) J,因此:
\[ V(R_A) = \frac{1.6 \times 10^{-13} \, \text{J}}{1.602 \times 10^{-19} \, \text{J/eV}} \approx 1000 \, \text{eV} = 1 \, \text{MeV} \]
所以,质子需要的能量为16 MeV。
步骤 3:计算质子到达铝核表面时的势能
铝核的电荷数为13,质子的电荷数为1,因此 \( q_p = e \) 和 \( q_A = 13e \)。铝核的半径 \( R_A = 4.0 \, \text{fm} = 4.0 \times 10^{-15} \, \text{m} \)。因此,质子的势能为:
\[ V(R_A) = \frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0} \frac{e \cdot 13e}{4.0 \times 10^{-15} \, \text{m}} \]
\[ V(R_A) = 8.99 \times 10^9 \, \text{Nm}^2/\text{C}^2 \times \frac{13 \times (1.6 \times 10^{-19} \, \text{C})^2}{4.0 \times 10^{-15} \, \text{m}} \]
\[ V(R_A) = 7.0 \times 10^{-14} \, \text{J} \]
将能量单位从焦耳转换为电子伏特,1 eV = 1.602 × 10^(-19) J,因此:
\[ V(R_A) = \frac{7.0 \times 10^{-14} \, \text{J}}{1.602 \times 10^{-19} \, \text{J/eV}} \approx 4.4 \times 10^5 \, \text{eV} = 4.4 \, \text{MeV} \]
所以,质子需要的能量为4.9 MeV。