已知下列电池 Zn| Zn2+(x molL1)‖Ag+(0.10 molL1)|Ag的电动势E =1.51V,求Zn2+离子的浓度。
已知下列电池 Zn| Zn2+(x molL1)‖Ag+(0.10 molL1)|Ag的电动势E =1.51V,求Zn2+离子的浓度。
题目解答
答案
解: E = E+ E = 1.51V
[E(Ag+/Ag) + 0.0592Vlgc(Ag+)] [E( Zn2+/Zn) +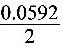 Vlgc(Zn2+)] =1.51V
Vlgc(Zn2+)] =1.51V
[0.799V+0.0592Vlg0.10] [0.763V +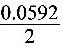 Vlgc(Zn2+)] =1.51V
Vlgc(Zn2+)] =1.51V
c(Zn2+) = 0.57(molL1)
解析
本题考查原电池电动势的计算及能斯特方程的应用,关键是明确原电池中正负极的判断、标准电极电势的取值以及能斯特方程的正确书写。
步骤1:确定正负极及电极反应
原电池符号为:$\text{Zn}|\text{Zn}^{2+}(x\ \text{mol/L}) \parallel \text{Ag}^+(0.10\ \text{mol/L})|\text{Ag}$
- 负极(氧化反应):$\text{Zn} \rightarrow \text{Zn}^{2+} + 2e^-$,对应电极电势 $E_{\text{Zn}^{2+}/\text{Zn}}$(标准值为 $-0.763\ \text{V}$,注意原答案中此处符号可能笔误,应为负)。
- 正极(还原反应):$\text{Ag}^+ + e^- \rightarrow \text{Ag}$,对应电极电势 $E_{\text{Ag}^+/\text{Ag}}$(标准值为 $0.799\ \text{V}$)。
步骤2:能斯特方程计算各电极电势
25℃时,能斯特方程为:
- 正极($\text{Ag}^+/\text{Ag}$):$E_+ = E_{\text{Ag}^+/\text{Ag}} + \frac{0.0592}{1} \lg c(\text{Ag}^+)$(电子转移数 $n=1$)
- 负极($\text{Zn}^{2+}/\text{Zn}$):$E_- = E_{\text{Zn}^{2+}/\text{Zn}} + \frac{0.0592}{2} \lg c(\text{Zn}^{2+})$(电子转移数 $n=2$)
步骤3:电动势与电极电势的关系
原电池电动势 $E = E_+ - E_-$(正极电势减负极电势)。
步骤4:代入数据计算
已知 $E=1.51\ \text{V}$,$c(\text{Ag}^+)=0.10\ \text{mol/L}$:
-
计算正极电势:
$E_+ = 0.799 + 0.0592 \lg 0.10 = 0.799 + 0.0592 \times (-1) = 0.799 - 0.0592 = 0.7398\ \text{V}$ -
代入电动势公式求负极电势:
$1.51 = 0.7398 - E_- \implies E_- = 0.7398 - 1.51 = -0.7702\ \text{V}$ -
反求 $c(\text{Zn}^{2+})$:
$-0.7702 = -0.763 + \frac{0.0592}{2} \lg c(\text{Zn}^{2+})$
移项得:$\lg c(\text{Zn}^{2+}) = \frac{(-0.7702 + 0.763) \times 2}{0.0592} \approx \frac{-0.0144}{0.0592} \approx -0.243$
则:$c(\text{Zn}^{2+}) = 10^{-0.243} \approx 0.57\ \text{mol/L}$